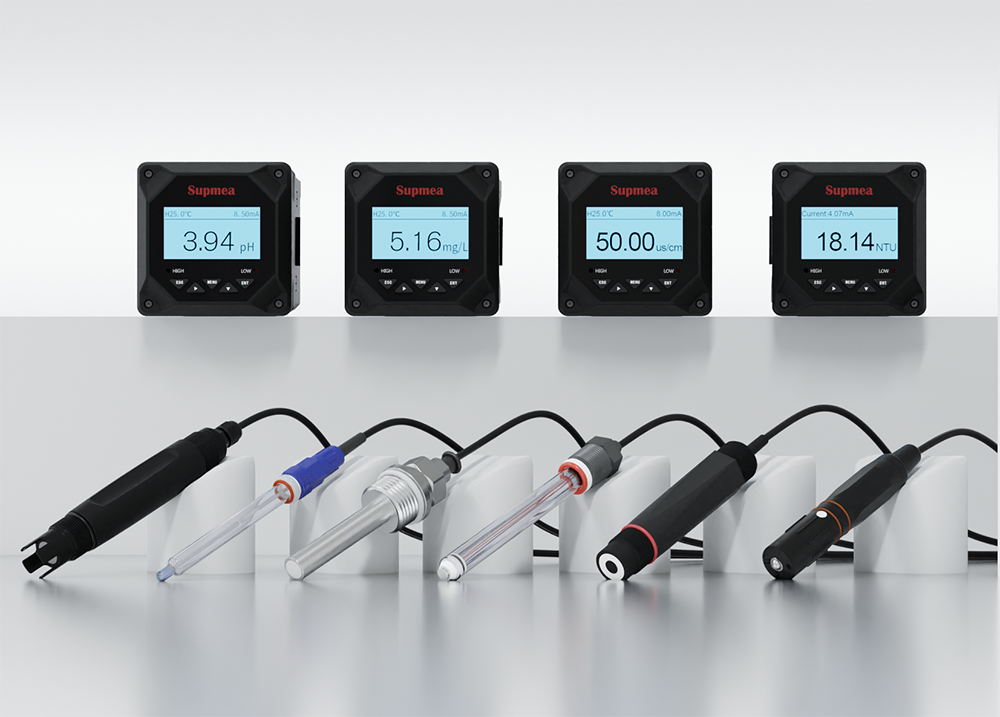
A Collection of All Types of Conductivity Meters
In the modern landscapes of industry, environmental monitoring, and scientific research, the precise understanding of fluid composition is paramount. Among the fundamental parameters, electrical conductivity (EC) stands out as a crucial indicator, offering vital insights into the total concentration of dissolved ionic material within a solution. The instrument that empowers us to quantify this property is the conductivity meter.
The market offers a diverse array of conductivity meters, ranging from sophisticated laboratory instruments to convenient field tools and real-time process monitoring devices. Each type is engineered to fulfill distinct missions. This guide will take you on a comprehensive journey through the design philosophies, core advantages, critical technological nuances, and unique applications of various conductivity meter types, providing a detailed resource for selecting and utilizing conductivity measurement equipment effectively.
I. The Core Components of Conductivity Meters
Before delving into the specific conductivity measurement types, let’s explore the fundamental elements common to all conductivity meters, which will make the selection of a conductivity meter for water or other liquids much easier:
Conductivity Sensor (Probe/Electrode)
This is the part that directly interacts with the solution under test, sensing changes in electrical conductance or resistance between its electrodes to gauge ion concentration.
Meter Unit
This electronic component is responsible for generating a precise alternating current (AC) voltage, processing the signal from the sensor, and converting the raw measurement into a readable conductivity value.
Temperature Sensor
Conductivity is highly sensitive to temperature variations. Often integrated within the probe, the temperature sensor continuously monitors the solution’s temperature and applies necessary temperature compensation, ensuring the accuracy and comparability of measurement results.
II. The Operational Principle of Conductivity Meters
The function theory of a conductivity meter relies on a precise electronic and electrochemical process that measures a solution’s ability to carry an electric current.
Generating the Current
The meter initiates the process by applying a stable alternating current (AC) voltage across the electrodes of its sensor (or probe). When the sensor is immersed in a solution, dissolved ions (cations and anions) are free to move. Under the influence of the electric field created by the AC voltage, these ions migrate toward the oppositely charged electrodes, creating an electric current that flows through the solution. The use of AC voltage is crucial because it prevents electrode polarization and degradation, which would otherwise lead to inaccurate readings over time.
Calculating Conductance
The meter unit then measures the magnitude of this current (I) flowing through the solution. Using a rearranged form of Ohm’s Law (G = I / V), where V is the applied voltage, the meter calculates the solution’s electrical conductance (G). Conductance is a measure of how easily current flows between the specific electrodes in a specific volume of liquid.
Determining Specific Conductivity
To obtain the specific conductivity (κ), an intrinsic property independent of the probe’s geometry, the measured conductance (G) must be normalized. This is achieved by multiplying the conductance by the probe’s fixed cell constant (K). The cell constant is purely a geometric factor defined by the distance between the electrodes and their effective surface area. The final, specific conductivity is thus calculated using the relationship: κ = G·K.
III. All Types of Conductivity Meters
Based on application scenarios and required measurement precision, conductivity meters can be broadly categorized. This post collects them all and walks you through them one by one for a detailed understanding.
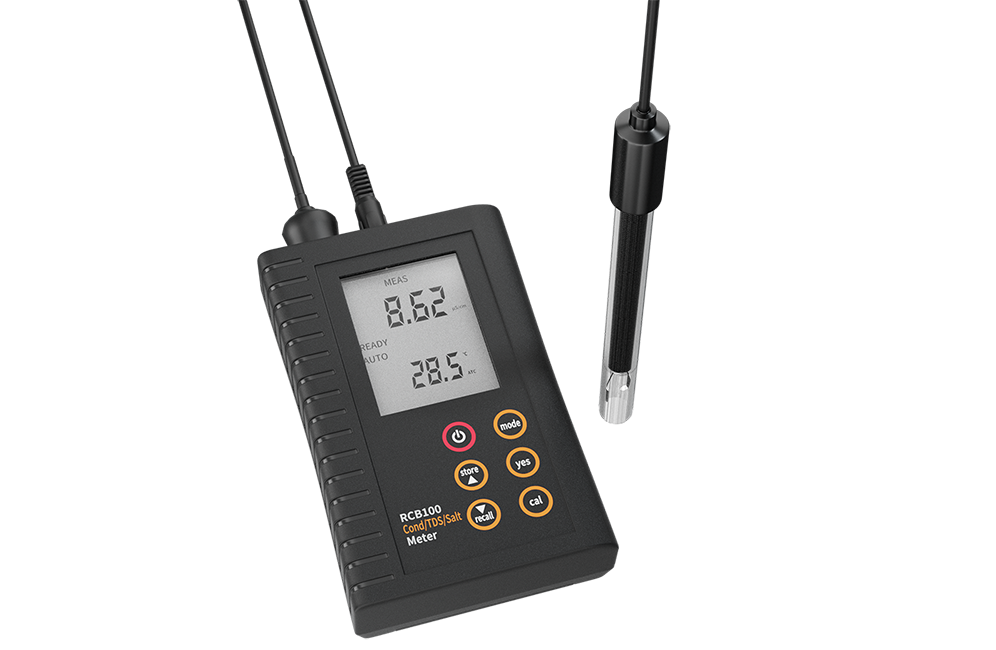
1. Portable Conductivity Meters
Portable conductivity meters are specialized analytical instruments engineered for high-efficiency, on-site diagnostics. Their fundamental design philosophy prioritizes a critical trifecta: lightweight construction, robust durability, and exceptional portability. This feature ensures that laboratory-grade measurement precision is reliably delivered directly at the sample solution source, which effectively minimizes logistical delays and maximizes operational flexibility.
These instruments are specifically built for demanding fieldwork. To achieve sustained performance under harsh outdoor and industrial conditions, they feature battery-operated power and are meticulously engineered with dust-proof and waterproof designs (often specified by an IP rating). The meters significantly boost operational efficiency in the field by offering rapid response times for instant results, coupled with integrated data logging capabilities. This combination makes them the definitive choice for rapid water quality assessment across remote geographical locations and expansive industrial production floors.
Wide Applications of the Portable Conductivity Meter
The flexibility and durability of portable conductivity meters make them indispensable across several key sectors:
1. Environmental Monitoring: The portable EC meters are essential tools for water quality assessment, performing surveys of rivers, lakes, and groundwater, and identifying pollution sources.
2. Agriculture and Aquaculture: These lightweight meters are used to monitor irrigation water, hydroponic nutrient solutions, and fish pond water quality to maintain optimal salinity and nutrient concentrations.
3. Industrial On-site Checks: The meters also provide rapid, preliminary testing of process waters, such as cooling tower water, boiler water, and industrial wastewater discharges.
4. Educational and Research Fieldwork: The convenience and ease of use features make these meters perfect for outdoor teaching and basic field experiments, offering hands-on data collection for students and researchers.
This probe’s versatility ensures the meter offers flexibility in diverse environmental settings, covering everything from relatively pure water to more saline solutions.
2. Bench-top Conductivity Meters
The benchtop conductivity meter is a specialized analytical instrument that represents the apex of electrochemistry instrumentation for demanding research and rigorous Quality Control (QC) environments. With high precision, multi-functional, and robust functions, this bench-top meter is centered on delivering uncompromised accuracy and stability, which ensures the integrity of critical analytical data.
The centural systems of the EC meter utilize high-resolution circuitry and premium sensors to guarantee superior measurement accuracy, fundamentally reducing measurement uncertainty in critical analyses.
The benchtop conductivity meter is designed to maximize laboratory efficiency and ensure data reliability. With its workflow being streamlined through the multi-parameter measuring integration, this meter makes it possible for simultaneous measurement of core parameters like EC, TDS, and Salinity, and optional capabilities of pH, ORP, and ISE.
This consolidation acts as an all-in-one testing solution, boosting laboratory throughput. Furthermore, advanced data management (secure storage, export, print) ensures full compliance with GLP/GMP standards, providing traceable and audit-compliant data that minimizes regulatory risk.
Finally, optimal performance across diverse sample matrices, from ultrapure water to high-concentration solutions, is guaranteed through the flexible accommodation of various probe types and specific K-values (cell constants).
Wide Applications of Bench-top Conductivity Meters
This high-performance bench-top system is crucial for organizations requiring definitive, high-confidence analytical results:
1. Pharmaceutical & Food/Beverage QC: The bench-top meter is essential for rigorous quality control (QC) testing of both raw materials and final products, where regulatory compliance is non-negotiable. This directly supports searches related to “pharma water testing” and “beverage quality analysis.”
2. Research and Scientific Development (R&D): It provides the high precision necessary for new material validation, chemical synthesis monitoring, and process optimization.
3. Industrial Water Management: The bench-top meter is critical for precise water quality analysis across ultrapure water (UPW) systems, drinking water facilities, and industrial wastewater treatment, helping facilities maintain operational efficiency and environmental standards.
4. Chemical Laboratories: Utilized for fundamental tasks such as accurate solution preparation, chemical characterization, and high-precision titration endpoint determination, the meter forms the bedrock of laboratory accuracy.
3. Online/Industrial Conductivity Meters
The Online/Industrial Conductivity Meter is designed specifically for automated process environments. Centering on continuous, real-time monitoring, high reliability, and seamless integration into existing control architectures. The meter replaces manual sampling by providing 24/7 uninterrupted data streams, acting as the critical sensor node for process optimization and control. This instrument is essential where continuous monitoring of water quality or solution concentration is vital for maintaining product quality, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
The Online/Industrial Conductivity Meter offers tangible benefits that ensure operational excellence in demanding environments.
The meter guarantees real-time process control by enabling the immediate detection of process anomalies with its 24/7 uninterrupted data, ensuring rapid response times that save costs and prevent downtime. Its rugged construction makes it reliable; both the sensor and transmitter feature industrial-grade construction, resistant to corrosion and fouling, making the meter ideally suited for harsh operating conditions and reducing the maintenance burden.
Furthermore, the meter ensures seamless PLC/DCS system integration by supporting standard 4-20mA analog outputs alongside crucial digital protocols like Modbus and Profibus. The meter minimizes maintenance through advanced sensor technology, frequently utilizing inductive (toroidal) sensors. These non-contact sensors prevent electrode erosion and buildup, making the meter indispensable for challenging media (e.g., corrosive or fouling solutions). Finally, for critical purity applications like ultrapure water systems, the meter maintains precision using specialized high-purity probes (e.g., sensitive 2-electrode probes with low cell constants) to reliably detect trace ionic contaminants.
Designed specifically for automated process environments, this series of Online/Industrial Conductivity Meters embodies a design philosophy centered on continuous, real-time monitoring, high reliability, and seamless integration into existing control architectures.
These rugged, dedicated instruments replace manual sampling with 24/7 uninterrupted data streams, acting as the critical sensor node for process optimization, control, and safeguarding expensive equipment. They are essential for any operation where continuous monitoring of water quality or solution concentration is vital for maintaining product quality, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
These industrial-grade meters offer tangible benefits for professionals seeking reliable, low-maintenance online analytical tools:
Guaranteed Real-Time Process Control
Providing 24/7 uninterrupted measurement data, these online industrial conductivity meters enable the immediate detection of process anomalies. This capability is paramount for searchers focused on “real-time process monitoring” and “instant anomaly detection,” ensuring rapid response times that save costs and prevent downtime.
Rugged Construction for Harsh Environments
Both the sensors and transmitters feature industrial-grade, robust construction. They are inherently resistant to corrosion and fouling, making them ideally suited for the most harsh operating conditions, significantly reducing the maintenance burden in challenging industrial settings.
Seamless PLC/DCS System Integration
The online conductivity meters are engineered for maximum compatibility, supporting standard 4-20mA analog outputs alongside crucial digital protocols like Modbus and Profibus. This facilitates seamless integration with PLC/DCS systems, essential for users searching for “automated industrial sensor integration” solutions.
Minimizing Maintenance with Advanced Sensor Technology
A key advantage is the frequent use of advanced sensor technology, particularly inductive (toroidal) sensors. These non-contact sensors prevent electrode erosion and buildup, making them indispensable for challenging media, such as highly corrosive, viscous, or fouling solutions. This dramatically reduces maintenance and extends operational life in critical processes like concentrated acid/base monitoring or boiler blowdown control.
Precision for Critical Purity Applications
For extremely demanding scenarios, such as ultrapure water (UPW) systems in power generation or semiconductor manufacturing, the use of specialized high-purity online probes is crucial. These are typically highly sensitive 2-electrode probes with very low cell constants (e.g., K=0.01/cm) designed to reliably detect even trace ionic contaminants.
Wide Applications of Online Industrial Conductivity Meters
The continuous monitoring capability of these instruments is leveraged across high-stakes industrial processes:
1. Industrial Water Treatment & Management: The online industrial meters are used to critically monitor the efficiency of Reverse Osmosis (RO) units, ion exchange systems, and EDI modules. They are also vital for continuous concentration management in boiler water and cooling towers, optimizing cycles of concentration and chemical usage.
2. Chemical Production & Process Control: Essential for online monitoring of acid/base concentrations, reaction progress tracking, and product purity verification, ensuring consistent chemical formulations and process yields.
3. High-Purity Manufacturing: Mandatory for equipment safety and product efficacy, these online instruments are critically deployed in pharmaceutical and power generation facilities for the rigorous, online monitoring of ultrapure water production, condensate, and feedwater quality, ensuring complete contamination control.
4. Food and Beverage Hygiene: Used for online control of CIP (Clean-in-Place) solution concentrations and precise product mixing ratios, the online conductivity meters meet the sanitation standards perfectly while minimizing water and chemical waste.
4. Pocket Conductivity Testers (Pen-style)
These pen-style conductivity testers are engineered for extreme portability, simple operation, and fast, indicative measurements. Rejecting complex lab setups, these ultra-compact conductivity measurements put instant analytical power directly into your pocket. They are the go-to solution for users requiring quick, on-the-go water quality assessments without the need for high-precision, audited data. This tool is perfect for enabling immediate, actionable insights into general solution purity and concentration.
These pocket meters appeal to a broad market by offering unparalleled convenience and value:
Unmatched Portability
Ultra-compact and pen-sized design ensure that they can be easily carried and used for true on-the-go, anytime, anywhere measurements.
Plug-and-Play Simplicity
Designed for maximum user accessibility, these pen EC testers feature simple operation, typically involving just one or a few buttons by providing plug-and-play functionality.
Cost-Effective Water Testing
Generally positioned at a lower price point, these devices are cost-effective, making high-quality water testing accessible to budget-conscious users and the general public, fulfilling searches for “affordable TDS meter” or “cheap water tester.”
Quick TDS Estimation
Many pocket EC meters offer direct TDS readings alongside Electrical Conductivity (EC). While based on a default conversion factor, this feature provides a quick estimation for general water quality checks.
Wide Applications of Pen EC Meter
The ultra-compact pen-style conductivity tester is perfectly suited for small-room laboratories, tight growing operations, and field use where space efficiency is critical.
Consumer and Home Water Use: Ideal for simple testing of drinking water purity, aquarium water health, or swimming pool water quality. This is a primary target for homeowners and hobbyists.
Small-Scale Hydroponics and Gardening: Used for basic checks of nutrient solution concentrations, providing amateur and small-scale growers with essential data to manage plant health without specialized equipment.
Educational and Outreach Programs: Their simplicity and low cost make them perfect teaching tools to help students and the public understand the concept of conductivity and its relation to water dissolved solids.
IV. Factors to Consider when Choosing a Conductivity Meter
When choosing a conductivity meter, the selection must go with the specific needs of the applications for reliable results and efficient operation. Below are the significant factors that you ought to take into consideration during the EC meter selection:
Measurement Range and Accuracy
Measurement range and accuracy are the initial, fundamental considerations. You must confirm the instrument’s operational limits are suitable for the conductivity values of your target solutions.
Simultaneously, assess the required accuracy and precision; the meter’s technical specifications must align with the necessary level of detail for your quality standards or research objectives.
Environmental Factors
Beyond core measurement capability, environmental factors demand attention. Temperature compensation is an essential feature if the solution or ambient conditions fluctuate, as it automatically corrects readings to a standard reference temperature, ensuring consistency.
Furthermore, the selection of the correct probe is non-negotiable, anyway, different probe types are optimized for distinct applications and media. Choosing a probe that is both chemically compatible with the tested purpose and physically suited to the tested environment is critical for longevity and performance.
Operational Efficiency and Data Integration
Last but not least, the operational efficiency and data integration should be taken into consideration. The User Interface should include intuitive controls and a clear display to minimize training time and potential errors.
Then, assess your connectivity requirements: determine if you need data logging, external device communication, or seamless integration with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) for streamlined reporting and compliance.
FAQs
Q1. What is conductivity?
Conductivity refers to the ability of a substance to conduct an electric current. It is a measure of the concentration of ions present in a solution.
Q2. What units are used to measure conductivity?
Conductivity is typically measured in Siemens per meter (S/m) or microsiemens per centimeter (μS/cm).
Q3. Can a conductivity meter measure the purity of water?
Yes, conductivity meters are commonly used to assess the purity of water. Higher conductivity values can indicate the presence of impurities or dissolved ions.
Q4. Are conductivity meters suitable for high-temperature measurements?
Yes, some conductivity meters are designed to withstand high temperatures and can accurately measure conductivity in hot solutions.
Q5. How often should I calibrate my conductivity meter?
The calibration frequency depends on the specific meter and its usage. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for calibration intervals.
Post time: Nov-05-2025