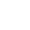What is a pH Meter? [Definition, Working Theory, Applications]
pH is not a complicated concept in everyday life, provided that we encounter it across a wide range of applications. From laboratory experiments to industries such as water treatment, power generation, food and beverage processing, and hydroponics, the pH scale plays a critical role in quality control and process performance.
This article provides a clear introduction to pH and pH meters, explains the working principle of pH meters, illustrates the types of pH meters, and explores their practical applications. By reading this guide, you will gain a solid understanding of how pH meters work and their common applications.
Table of Contents:
- 1. What is the pH value?
- 2. What is a pH meter used for?
- 3. Types of pH meters
- 4. Applications of the pH meters
What is the pH value?
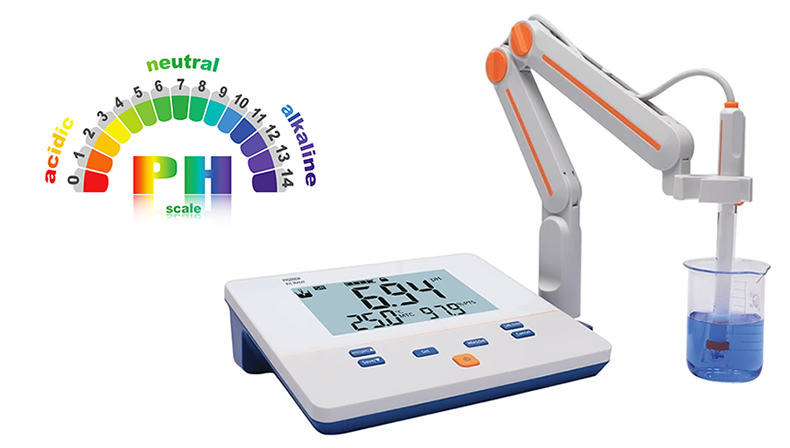
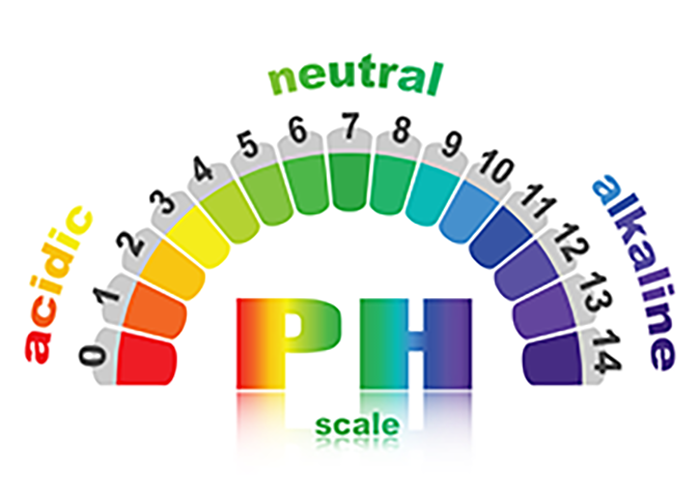
pH, with the full form of potential of Hydrogen, is a value between 0 and 14 that indicates the acidity or alkalinity of a liquid or solution. As 7 is the neutral pH value, the solution is marked as acidic if tested under 7 and alkaline if measured above 7. Every little subtle change in the pH value will result in a change in the property of acidic or alkaline.
This value is of vital importance due to its fundamental influence on chemical reactions, nutrient availability, and biological activity in solutions, which is widely used in various applications like water quality testing, industrial processing, agriculture, food and beverage, and hydroponics. Understanding this significant value helps ensure the solid treatment of liquids and maintains the superior quality of the products.
What is a pH meter used for?
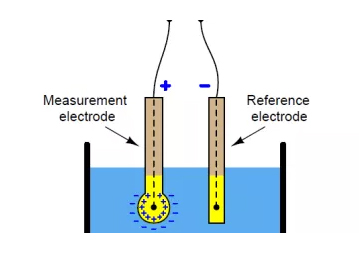
A pH meter is an instrument configured with a sensor electrode and a reference electrode to measure the pH value of the targeted solution.
The reference electrode is made of saturated KCl solution, while the sensor electrode contains a buffer solution with a pH of 7, and the silver wire coated with silver chloride is immersed in these two solutions. At the end of the measuring electrode is a bulb made of porous glass coated with silica and metal salt.
After the bulb of the sensor electrode contacts the solution, the hydrogen ions in the solution will replace the metal ions on the bulb. This substitution of metal ions causes current to flow in the metal wire, which is read by a voltmeter.
This pH measurement also works in the pH controller, pH transmitter, pH sensor, and so on, even though there are certain differences between the meter, controller, and transmitter.
How does a pH meter work?
A pH meter measures acidity or alkalinity based on the electrochemical principle of a galvanic cell. It uses two electrodes, a sensor electrode and a reference electrode, just as mentioned above, to detect the electrical potential generated when they are immersed in a solution. According to Nernst’s law, this electrical potential is directly related to the concentration of hydrogen ions in the liquid.
As the hydrogen ion concentration changes, the voltage between the two electrodes changes accordingly. The pH meter converts this voltage signal into a pH value, which is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. This allows the instrument to provide a fast and accurate measurement of a solution’s pH.
During pH measurement, factors such as solution temperature and ionic strength should be considered, as they can influence electrode response and measurement accuracy.
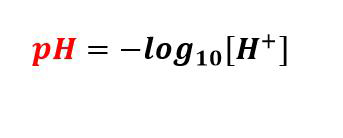
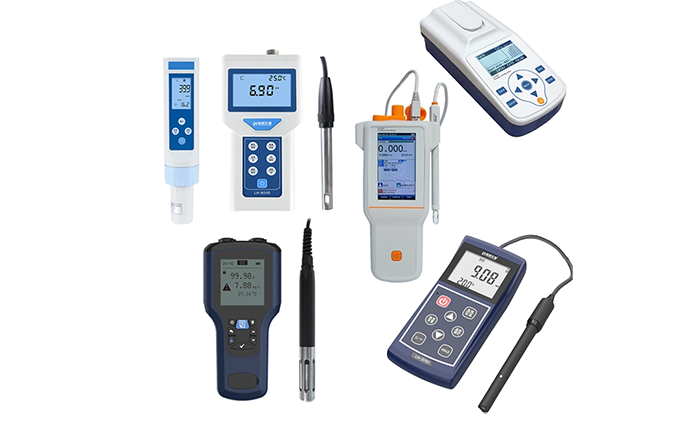
Types of pH meters
Aimed to meet different measuring purposes in various applications, pH meters are manufactured with different configurations and settings. Below are the most common types of pH meters, categorized by their structure, usage environment, and measurement requirements.
Portable pH meters
Just as its name suggests, the portable pH meter is widely welcomed where the convenience and portability are highly considered. With the battery soldered, this type of pH meter is simply operated and calibrated.
Usually configured with a built-in electrode or detachable electrode, the portable pH meters are ideal for water quality testing, soil pH measurement, aquaculture, agricultural research, environmental monitoring, and other applications where carrying a benchtop system is impractical.
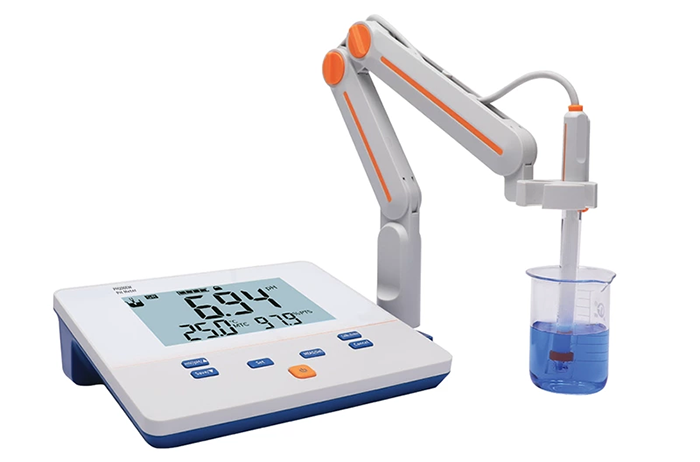
Benchtop pH meters
Benchtop pH meters always come with a large display with advanced functions, which support data logging and connectivity like USB/RS-232, eliminating extra data transfer and analysis.
Built with an automatic temperature compensation function, the instrument offers more accurate and precise pH readings by balancing the temperature’s influence on the pH measurement.
These stationary units are commonly seen in educational labs, research institutions, industrial labs, and production facilities where high accuracy and repeatable results are required.
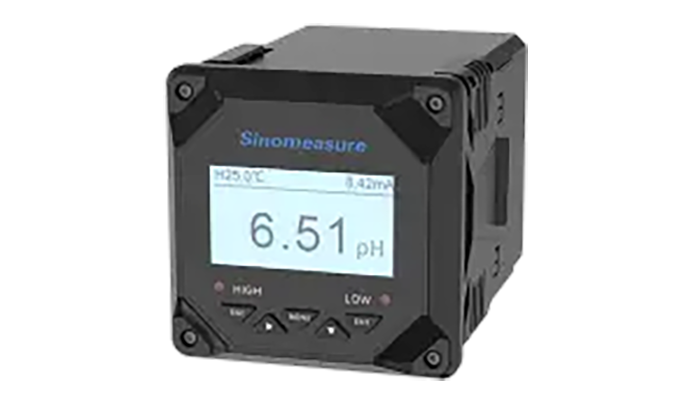
Online (Industrial) pH meters
The online or inline process pH meters are the pH measurement and monitoring instruments installed in the piping systems, tanks, or reservoirs directly with a waterproof and rugged design. These meters are designed for continuous monitoring in the process environment to provide real-time pH data for control systems or displays.
Via the connection of 4-20 mA, Modbus, or other protocols, the online meters are widely used in water and wastewater treatment, chemical processing, food and beverage production, boiler/tower water control, and any automated system requiring constant pH feedback.
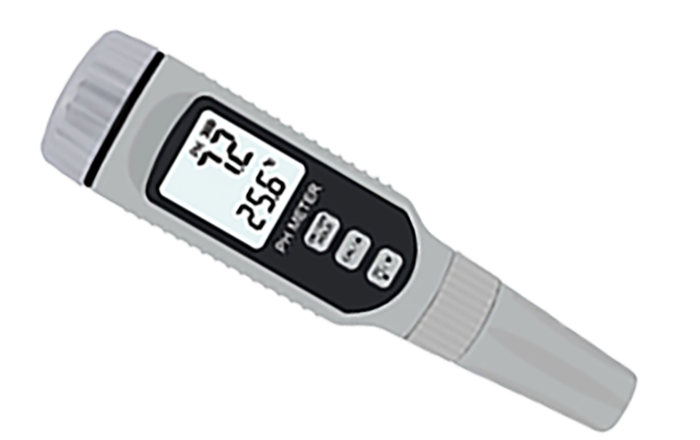
Pen-type pH meters
The pen-style or pocket pH meter is slim, just like a pen that you can put in your pocket. With the single-button operation, this pen-form pH meter can provide basic display functionality and limited calibration.
Typically lower in cost and easy to operate, these meters are often used by hobbyists in small hydroponic setups, pool testing, classroom demonstrations, and quick checks where ultra-precise control is not critical.
Applications of the pH meters
pH meters are widely used across many industries and scientific fields where accurate measurement of acidity and alkalinity is essential. Here are the industries where you can discover pH meters’ presence most often:
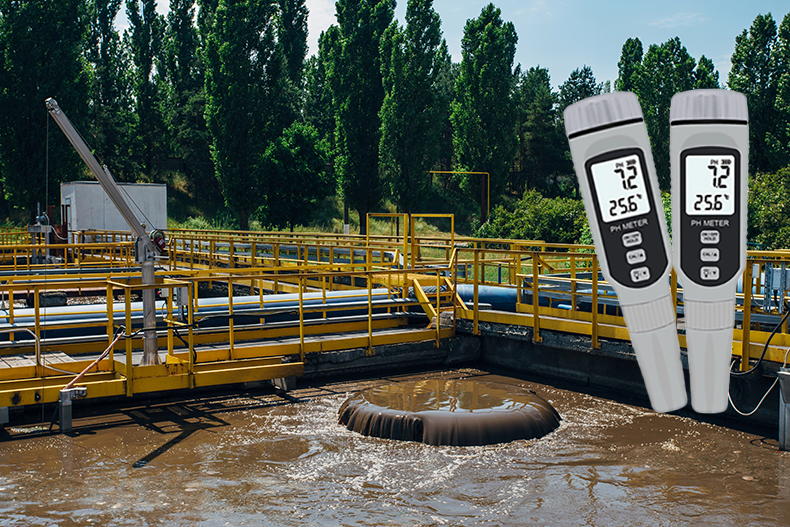
Water and wastewater treatment
Water and wastewater treatment is a big part of environmental processing, whereas pH meters are mostly deployed to monitor raw water, drinking water, and wastewater to ensure treatment processes run efficiently and meet the regulatory standards. On top of that, proper pH control helps protect equipment and optimize chemical dosing.
Agriculture and soil analysis
In agriculture, pH meters are used to measure soil and irrigation water pH since maintaining the correct pH level improves nutrient availability and supports healthy crop growth.
Hydroponics and aquaculture
pH meters play a key role in hydroponic and aquaculture systems by monitoring nutrient solution and water conditions. Knowing how to maintain the pH level in hydroponics matters, as it determines the plants’ growth. Too high or too low pH levels may result in plant malnutrition or root rot.
Chemical and industrial processes
Many industrial processes depend on strict pH control to ensure reaction efficiency, product consistency, and equipment protection. pH meters are commonly used in chemical manufacturing, power generation, and metal processing.
Food and beverage industry
pH measurement is critical for food safety, fermentation control, and quality assurance. pH meters are used in beverage production, dairy processing, brewing, and food preservation.
Laboratories and research
In laboratories, pH meters are essential analytical tools for research, education, and quality control testing. They provide accurate and repeatable results for scientific experiments and material analysis.
Application of a pH meter in the open water area
Application of a pH meter in electroplating wastewater treatment
Application of an online pH Meter in industry
Post time: Dec-17-2025